In today’s connected world, mobile networks cannot work efficiently without Routing Area Update (RAU) – an essential process in cellular network architecture. Network optimization for an efficient user experience in the rapidly changing realm of mobile communication.
Revolutionizing Connectivity | The Evolution of RAU in Mobile Networks and the Dynamic Landscape of Location Communication
RAU allows for mobile devices to be constantly alerting the cellular network of their current location in real-time. It assists in making sure that communication runs smoothly and successfully. Routing Areas are significant for 2G; and 3G networks. Subdivide larger geographical areas into comprehensible zones. Since Routing Area Update is concerned with mobile technology that changes from time to time, the issues and opportunities associated with this change are also evident.
Revolutionizing Connectivity | Unraveling the Dynamics of Routing Area Update in Mobile Networks
This introduction will delve into the centrality of Routing Area Update in improving mobile network efficiency and connection. Its impact on resource management as well as its historical significance. As well as its current significance with regard to 4G and 5G networks. It is important to know how RAU works in order to understand the current advancements. This continues to determine the future of the world’s mobile communicational system.
Routing Area Update | Your Gateway to a Connected World
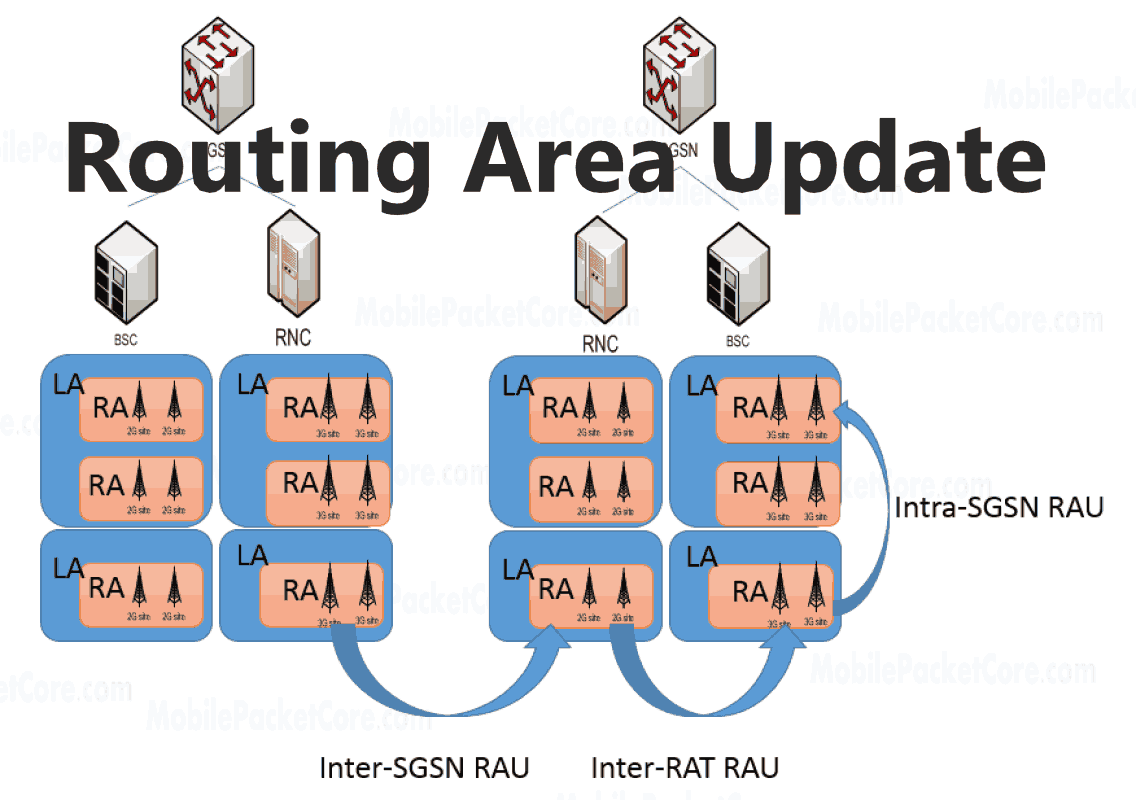
One such vital process, which takes place in the functioning of 2G and 3G cellular networks, is routing area update (RAU). This is key to efficient and reliable mobile communications. The idea of RAU originates from the arrangement of these older cellular networks as a Routing Area with several cells. In this article, we shall examine extensively what it is, the goals it aims to achieve, things that trigger it, how it occurs as well why it is significant.
Revolutionizing Connectivity | The Crucial Role of Routing Area Updates (RAU) in Seamless Mobile Network Management
In essence, RAU is an approach for mobile devices to indicate to the network their present location through an update of their Routing Area. The success of network management requires this process because it allows smooth cell changes or effective resource distribution. Hence, mobile devices will be continuously connected to the network and the role of RAU in sustaining such continuous access will be paramount.
Dynamic Mobility Management | Unraveling the Triggers of RAU Events in Mobile Networks
There are multiple catalysts for RAU events. Some of the major drivers include the relocation of the machine among others. The Routing Area Update is initiated by a mobile device during its movement from one Routing Area to another, in order to notify the network about the new location. Similarly, an RAU may also occur when the device turns on or is connected to the network. The network periodically and on an ‘event-driven’ basis receives the most up-to-date information about the location of the device.
Revolutionizing Location Updates | The Intricacies of RAU Process in Mobile Networks for Seamless Connectivity and Resource Optimization
Communication in this process takes place when the mobile device sends a message to the core infrastructure of the network. This might also include MSC which is common in 2G networks or SGSN found in 3G networks. The device should be able to decode this message and know his new Routing. It also allows the system to refresh its understanding of where exactly this device is within the network. Such updated location information is necessary for the effective transmission of calls as well as data to specific cells or Routing areas. As such it reduces unnecessary signaling and conserves network resources.
Routing Area Update | Paving the Way for Seamless Mobility and Network Efficiency
The main goal of RAU in 2G and 3G mobile networks has many important features for the efficiency of the cellular infrastructure. RAU, first and foremost is used by the network to update it on the latest position of a mobile device. Therefore this plays a very crucial role in achieving effective interoperability as mobile users transit. Each Routing Area consists of several cells within which they change their locations. Through executing the RAU, the mobile device advises the network on its novel destination. This helps in directing incoming calls, SMS, or data requests to the corresponding node (either cell or base station) within the Routing Area.
Revolutionizing Connectivity | Harnessing Real-Time Location Data for Dynamic Network Optimization
Network optimization greatly depends on routing area updates. Network operators are able to use the current location of mobile devices to determine their appropriate distribution of resources. The efficient allocation of network resources minimizes congestion and improves the quality of service. Network resources are utilized judiciously in the manner that they remain connected with the right cell and Routing Area when devices do so. These improve call quality and speed in the transmission of data.
Revolutionizing Connectivity | The Crucial Role of RAU Processes in Seamless Handovers
In connection with the handover procedures, the Routing Area Update process occurs. Such as when a mobile device moves from one cell to another, or from one Routing Area into another one. To ensure a smooth transition, the network kicks off the RAU. It should enable uninterrupted voice calls and data sessions over time. After the handover of the device’s connection to a new cell or Routing Area. Effective Routing area update and the handover process without any user moving with active call or session would experience a dropped call or a disruption of the same.
Fortifying Cellular Networks | RAU’s Cutting-Edge Security and Authentication Measures
Security and authentication provisions in routing area update. It ensures that only permitted gadgets will be allowed to penetrate into the wireless channel.
Fueling Seamless Mobility and Enhanced Network Efficiency
Routing Area Update (RAU) is very important for both 2g and 3g cell networks and offers many benefits. Most importantly, RAU serves as a supporting factor in keeping the network records up-to-date regarding their knowledge of the actual positioning of mobile phones. The geographical area is broken down into Routing Area which consists of more than one cell in a cellular network. An RAU occurs when a mobile device moves from one Routing area to another and hence the network is updated with these changes. Indeed, this data is important for the network to effectively utilize the available resources. There could be a situation where calls and data would be forwarded to the old site without RAI. This can cause delays in service delivery, especially when the network has stopped providing such services.
Revolutionizing Connectivity | RAU’s Dynamic Role in Network Efficiency and Resource Optimization for Seamless Communication
RAU facilitates the effective utilization of resources and efficient networking. Hence, by keeping their locations updated on a periodic basis or when moving to a new Routing Area. This implies that mobile devices are used to ensure resources such as frequencies and capacity are allocated appropriately on the network. This helps in the increased capacity for more people on the network. Maintaining service quality as congestion is reduced and seamless communication provided especially in highly crowded zones.
Revolutionizing Mobile Network Security | The Crucial Role of Routing Area Update in Authorizing and Safeguarding Device Access
In terms of security and authentication, RAU is important to make sure that mobile devices accessing the network should be permitted. Validation and security measures take place during the Routing Area Update verification procedure when certifying the device’s authenticity. This is a way of protecting the network and ensuring that only legitimate devices can utilize the services. This enhances the entire network’s stability and security.
Navigating the Evolution of Threats in RAU Processes through Advanced Security Measures
Another challenge is network security. With advancing mobile network technology, so do the risks. User privacy as well as integrity can be compromised when security vulnerabilities are exploited in Routing Area Update processes. Such attempts also include incorporating more advanced authentication procedures and encryption techniques for increased security of RAU.
Revolutionizing Connectivity | Navigating the Evolution from 4G to 5G Networks and the Transformative Shift in Radio Access Unit Paradigms
The development of 4G and 5G systems has been a key factor in the revival of its idea. Such network architecture has principles unlike tracing areas rather than trace routing areas. And introduce new, effective ways of locating mobile devices and controlling mobility. In time the legacy problems related to Routing Area Update in aged networks would matter less when adoptions of 4G and 5G are adopted.
What We’ve Discovered about Routing Area Update
Therefore, Routing Area Updates (RAU) are one of the most important features in 2G and 3G cellular networks. These help in effective network planning, locating, resource deployment, and call path-finding The outlined processes are of paramount importance since they have ensured uninterrupted and smooth mobile communication.
Nonetheless, as a result of 4G and 5G technologies and the growing demands for interconnectivity, the notion behind Routing Areas is being reshaped. Challenges and developments in RAU will also continue even as networks keep maturing and diversifying. The continuous enhancements of security, scalability, energy efficiency, and transition towards sophisticated network architectures. it envisions the future of RAU such that the university keeps up with the modern era. Nevertheless, be it 2G, 3G, 4G, or even 5G, there is nowhere else such as here that ensures smooth communication connections.
From Roadblocks to Horizons | Charting the Future
While it serves an important role in cellular networks, routing area update (RAU). Additionally, it faces many challenges which lead to continuous improvement efforts. Among these major issues is the increasing pressure on wireless network systems. Growth in the number of connected devices and the explosion of data consumption. The need for effective management of RAU events can be brought about by bandwidth-intensive applications, such as the IoT. However, the task of maximizing RAU procedures to accommodate these requirements while maintaining the quality of the network is a big problem to overcome.